
AI Mistakes in Finance: What a 5% Risk Really Means
AI mistakes in finance aren’t theoretical, they’re real, measurable, and increasingly costly. That seemingly small 5% risk? It can translate into massive losses when scaled across automated systems and high-stakes portfolios. This post breaks down what that figure truly means—and what you can do to stay protected.
Key Takeaways:
- AI is transforming the financial sector but poses significant risks when left unchecked.
- Small AI Mistakes in Finance (“A Five Percent Risk”) can lead to major financial losses.
- Bias in AI models can result in unfair finance and investment decisions.
- Governments are introducing strict AI regulations, businesses must adapt.
- Financial institutions must blend and use AI efficiency with human oversight.
Understanding The Risk of AI Mistakes in Finance
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and generative AI is rapidly reshaping the financial services industry, enabling faster trades, automated loan approvals, and predictive analytics. However, even the most intelligent systems are prone to mistakes. A “Five Percent Risk” refers to the risks associated with AI driven models that make small yet costly miscalculations that, when scaled, result in billion-dollar losses.
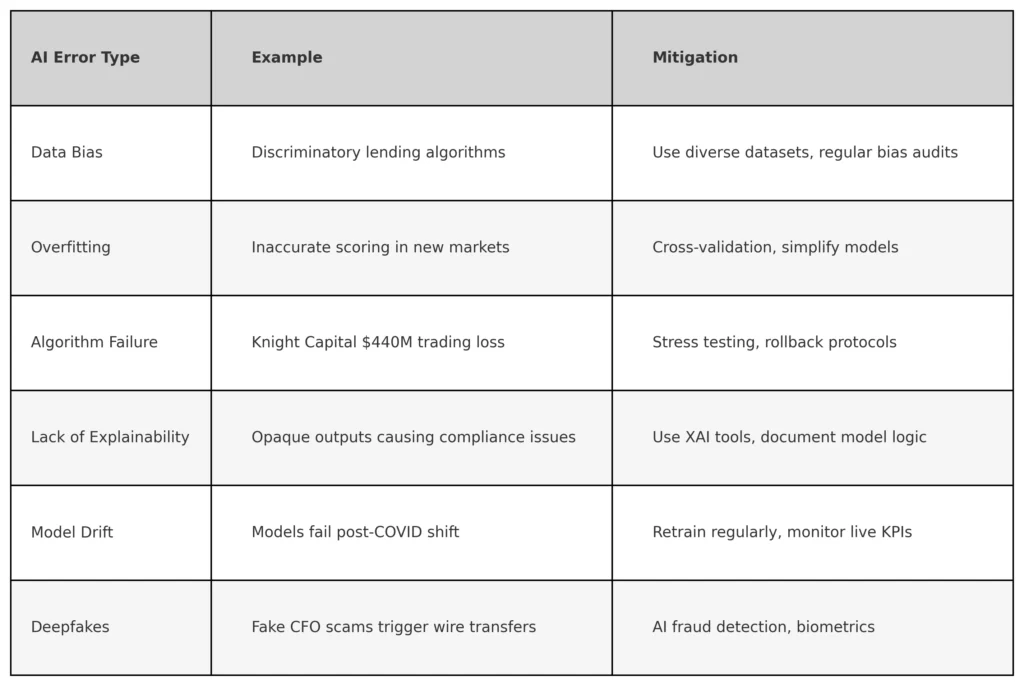
In 2012, Knight Capital lost $440 million in just 45 minutes due to a malfunctioning algorithm, one of the most dramatic early examples of how AI mistakes in finance can threaten institutional stability. More recently, JPMorgan Chase came under scrutiny after its AI-powered email outreach system misfired, delivering inappropriate messages to high-net-worth clients and raising fresh concerns about the unpredictability of AI in customer engagement.
As AI systems grow more integrated into trading, risk management, and client communications, the stakes rise. not just in technical errors, but also in exposure to AI-enabled fraud. From deepfake executive impersonations to synthetic identity attacks, detecting and preventing AI-driven fraud has become as crucial as avoiding internal system errors.
The Cost of AI Mistakes in Finance
A minor error in an AI-enhanced trading algorithm can create volatility. Misinterpreted data can lead to unnecessary sell offs or high risk investments. In banking, flawed AI credit scoring can deny eligible borrowers while approving high risk applicants, increasing loan defaults. AI threats in finance is not just theoretical, it has already caused significant damage.
For example, in 2021, an AI-powered glitch at Citigroup caused a “flash crash” in European markets, wiping billions off the stock market within minutes before rebounding. Similarly, in 2018, an Artificial Intelligence model used by Amazon to automate hiring was found to systematically discriminate against female applicants, leading to legal and reputational consequences.
AI Mistakes in Finance: Key Risks of AI Adoption in Financial Services
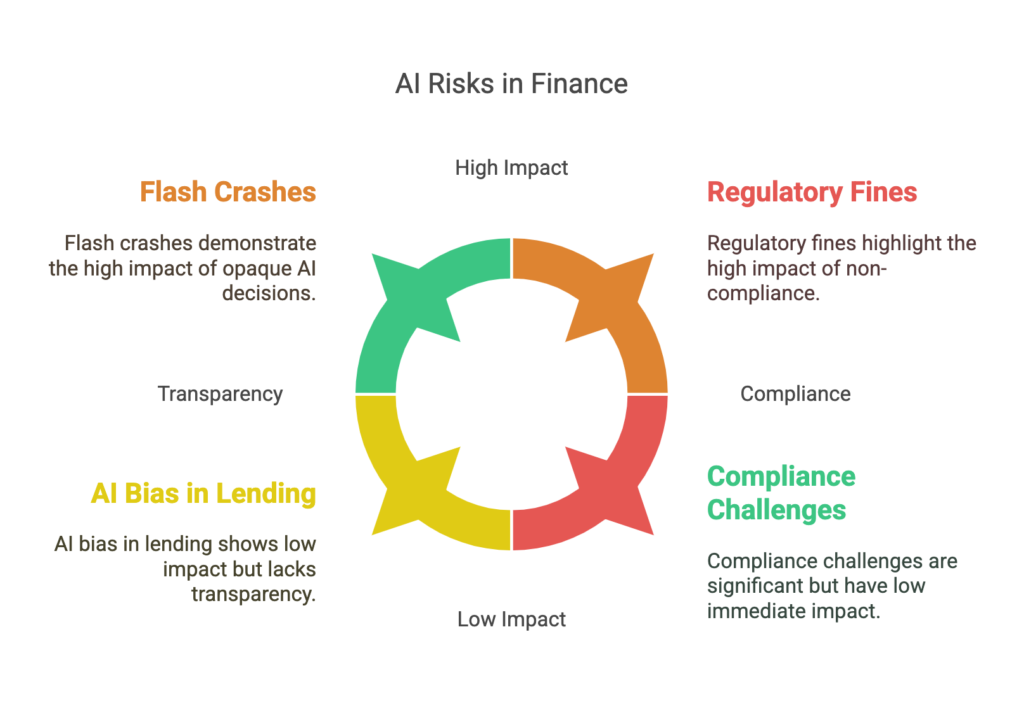
1. The “Black Box” Problem
Many Artificial Intelligence and machine learning models operate as “black boxes,” meaning their decision-making processes are not transparent. If a bank denies a loan or an investment firm makes a major trade based on AI predictions, financial professionals must be able to justify the reasoning. Otherwise, accountability becomes a nightmare.
The EU’s AI Act aims to address this by requiring financial institutions to use explainable AI (XAI) models. However, compliance remains a challenge for firms reliant on deep learning models.
2. Algorithmic Trading Gone Wild
AI-assisted trading risks explained: High-frequency trading (HFT) algorithms make thousands of trades per second. However, if AI misreads market conditions, it can trigger flash crashes. In 2010, the “Flash Crash” wiped out nearly $1 trillion in market value within minutes due to algorithmic mistakes.
Another example is the 2018 volatility spike when AI-enabled trading funds misinterpreted market movements, causing massive sell-offs and wiping out billions in investor wealth in a matter of hours.
3. Bias in Lending & Credit Scoring
AI technologies learns from historical data, and if that data contains biases, AI tools will perpetuate them. This has led to cases of AI bias and regulations tightening around fairness in automated decision-making. For example, studies have found that AI-assisted loan approvals have discriminated against women and minority borrowers, even when financial profiles were identical to other applicants.
In 2022, a major U.S. fintech lender faced a lawsuit for AI-powered discrimination in mortgage approval. The AI system consistently rated minority applicants as higher risk despite equivalent financial credentials. As a result, regulatory bodies like the CFPB are pushing for more transparent AI credit models.
4. Compliance & Regulatory Challenges
Regulators are cracking down on AI-enhanced finance. The EU AI Act and various U.S. regulations demand transparency, fairness, and accountability. Institutions failing to comply with these guidelines face hefty fines and legal consequences. Keeping up with the evolving regulatory landscape is crucial for any financial entity utilizing AI.
In China, AI-powered financial services are now required to submit risk assessments to regulators, highlighting a global trend toward stricter oversight. Companies that fail to comply, such as Ant Group, have faced billions in fines and regulatory scrutiny.
How to Prevent AI Mistakes in Finance
✅ Human + AI Collaboration
AI should enhance, not replace, human financial experts. A “human in the loop” model ensures oversight of high-risk decisions, reducing the chances of costly AI mistakes.
For instance, Morgan Stanley has implemented AI-driven investment strategies but maintains a team of human analysts to verify AI-generated insights before executing trades.
✅ Explainable AI (XAI)
Companies must adopt AI that provides clear, auditable explanations for its decisions. Transparency in AI models builds trust and mitigates legal risks.
The U.S. SEC is now requiring financial institutions to disclose how predictive models are used in decision-making processes, emphasising the need for explainability in financial services.
✅ Stress Testing & Monitoring
Continuous monitoring and regular stress testing of AI systems can identify weaknesses before they escalate. Major finance institutions now conduct AI failure simulations to preempt market disruptions.
For example, the Federal Reserve has initiated AI stress testing frameworks for major finance companies, ensuring that automated systems do not contribute to systemic risks in financial markets.
✅ Adapting to New Regulations
Staying ahead of AI laws is critical to maintaining compliance and avoiding financial penalties. Financial leaders must actively engage with regulatory bodies to ensure their intelligent systems align with evolving legal standards.
Global organisations, including HSBC and Deutsche Bank, have formed AI governance committees to ensure their use of AI algorithms comply with national and international regulations.
Final Thought: Preventing AI Mistakes in Finance Requires Guardrails
AI is revolutionising finance, but it is not infallible. The “Five Percent Risk” is not just a theoretical concern, it is a real, costly issue that financial institutions must address. By integrating human oversight, prioritising transparency, and complying with AI regulations, businesses can harness AI’s potential while minimising catastrophic failures.
FAQ: AI Mistakes in Finance
1. What are common AI mistakes in finance?
Common AI mistakes in finance include data bias, overfitting of models, lack of explainability, and erroneous trade execution. These issues can lead to faulty risk assessments, regulatory breaches, or even large scale financial losses, as seen in the Knight Capital case.
2. How can firms mitigate AI errors?
Firms can reduce AI mistakes by implementing robust testing protocols, monitoring systems in real time, and integrating human oversight. Using explainable AI (XAI), auditing data sources, and embedding AI ethics into governance frameworks are key to minimising risk.
3. What industries are most at risk from AI mistakes in finance?
Investment banks, credit lenders, and insurance companies face the greatest exposure due to automation, model reliance, and fraud vulnerability.
4. Can AI help prevent its own mistakes?
Yes, AI systems with built in anomaly detection and feedback loops can flag errors in real time, but they still require human oversight.
5. What role does regulation play in managing AI risks in finance?
Global regulators are increasingly focused on AI accountability, requiring transparency, explainability, and risk governance frameworks.
Next Step: Manage AI Mistakes in Finance Before They Escalate
📢 Don’t let AI imperfections put your financial institution at risk. Take proactive steps today!
📅 Schedule Your AI Readiness Assessment wow and ensure your systems are safe, compliant, and optimized for success. Serving clients across the UK, Europe & Asia-Pacific
