Behavioral Biases in Investment Decision Making: 6 to Avoid in 2025

Ever made an investment decision you later regretted? You’re not alone. A staggering staggering 66% of investors admit that emotions influence their choices, often leading to missed opportunities and lower returns. In the high-stakes world of finance, understanding behavioral biases in investment decision making is no longer optional, it’s the key to unlocking your portfolio’s true potential.
Whether you’re a seasoned investor, a high-net-worth individual, or just starting to build your wealth, behavioral biases in investment decision making, can derail your strategy. They cloud judgment, disrupt long-term plans, and ultimately, impact your bottom line.
Behavioral finance isn’t just academic, it affects real portfolios and real outcomes. Investors often delay or avoid implementing portfolio rebalancing strategies due to loss aversion, confirmation bias, or anchoring on past gains. In this guide, we’ll uncover the most common behavioral traps, show how they sabotage smart portfolio decisions, and give you clear strategies to avoid them.
Understanding Behavioral Biases in Investment Decision Making
Think of behavioral biases in investment decision making as mental shortcuts. They’re systematic patterns that can lead us astray from rational judgment. While these shortcuts help us navigate daily life, investment decision bias can be a costly trap in the complex world of investment decision-making.
Behavioral finance, a fascinating blend of psychology and finance, shines a light on these biases. It acknowledges that we’re not always the rational actors traditional finance assumes us to be. Emotions, cognitive limitations, and even our social environment play a significant role in how we manage our money.
Real-World Impact:
- The Dot-Com Bubble: Imagine investors, fuelled by the fear of missing out (FOMO) and overconfidence, pouring money into internet companies, ignoring basic financial analysis. This herd behaviour led to devastating losses when the bubble burst.
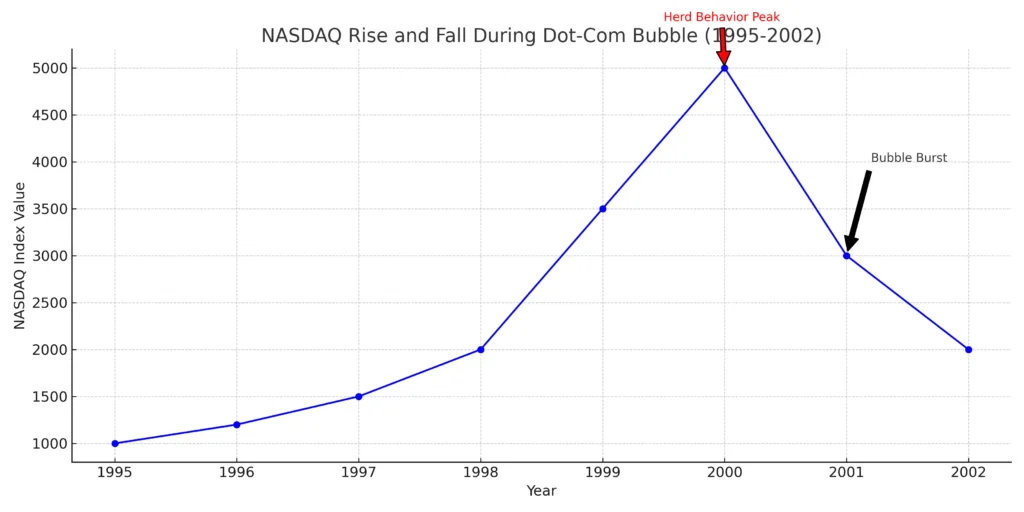
- The 2008 Financial Crisis: Confirmation bias – the tendency to seek information that confirms our beliefs – played a key role. Many investors downplayed the risks of subprime mortgages, leading to widespread financial devastation.
- Holding Losing Investments Too Long: The disposition effect, a common behavioral bias, causes us to sell winners too early and cling to losers, hoping for a rebound. This can severely damage portfolio performance.
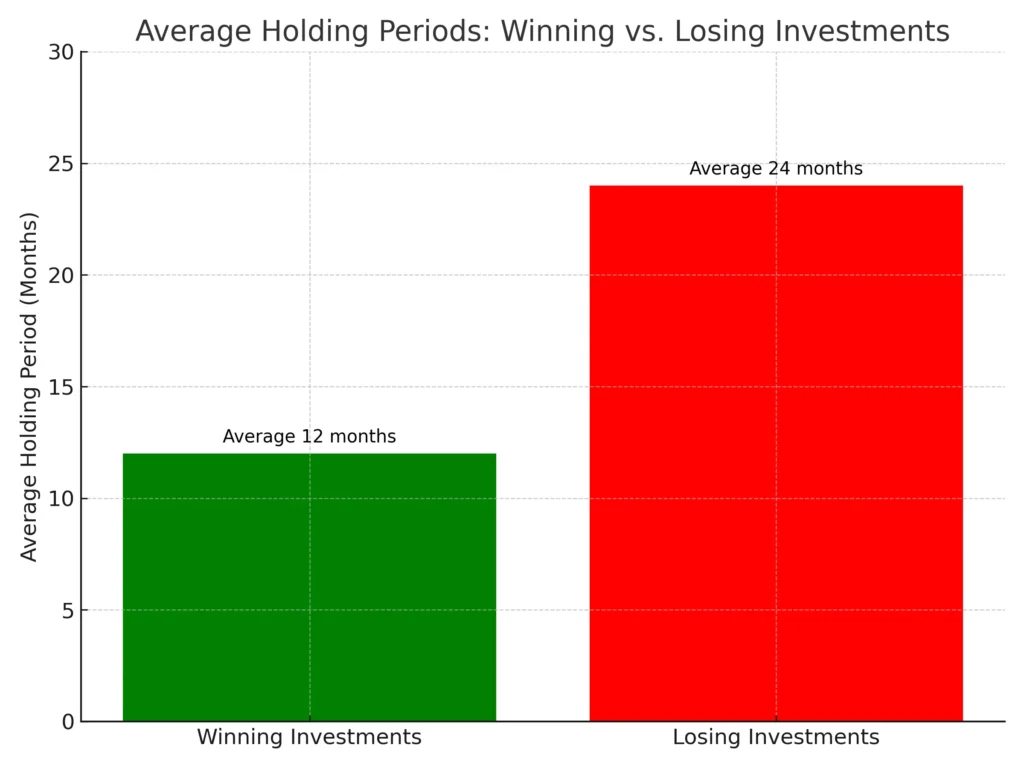
These examples aren’t just historical footnotes; they’re powerful reminders of how investment decision bias can impact your financial well-being.
Top Strategies to Overcome Behavioral Biases in Investment Decision Making
Combating behavioral biases in investment decision making requires a proactive, multi-faceted approach. Here’s how to take control:
Forge a Disciplined Investment Process
A rock-solid investment decision-making process is your best defense. This means:
- Crystal-Clear Investment Goals: Define your financial objectives. What are you saving for? What’s your risk appetite?
- Strategic Asset Allocation: How will you diversify your portfolio? Stocks, bonds, real estate? A well-defined plan is crucial.
- Scheduled Portfolio Rebalancing: Set a regular schedule (quarterly, annually) to rebalance your portfolio. This prevents emotional reactions to market swings.
- Written Rules: Having documented rules reviewed regularly.
Let Data Drive Your Decisions
Base your investment decisions on rigorous research and data analysis, not gut feelings or media hype. Use quantitative models and fundamental analysis to evaluate opportunities.
Cultivate Emotional Intelligence
Recognize your emotional state and how it might be influencing your judgment. Mindfulness techniques can enhance self-awareness.
Automate Where Possible
Consider automated investment platforms or tools that execute trades based on pre-set rules. This minimises emotional interference, especially for portfolio rebalancing.
Review, Learn, and Adapt
Regularly assess your investment performance. Identify instances where behavioral biases might have played a role. Learn from mistakes and refine your investment strategies.
6 Behavioral Biases in Investment Decision Making – How to Beat Them
Even with the best intentions, behavioral biases in investment decision making can be persistent. Here are common traps and how to avoid them:
- Overconfidence Bias: Overestimating your skills can lead to excessive risk-taking. Biases like overconfidence are dangerous.
- Solution: Actively seek out diverse perspectives and challenge your own assumptions.
- Confirmation Bias: Only seeing information that confirms your beliefs can lead to skewed financial decision-making.
- Solution: Deliberately seek out contradictory evidence and consider alternative viewpoints.
- Loss Aversion: Feeling the pain of a loss more strongly than the joy of a gain can lead to holding onto losing investments for too long.
- Solution: Focus on the long term and avoid impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations. Consider stop-loss orders.
- Herding: Following the crowd, even when it contradicts your analysis, can be disastrous.
- Solution: Trust your research and stick to your investment plan, even when it’s unpopular.
- Anchoring Bias: Over-relying on the first piece of information you receive can distort your judgment.
- Solution: Gather information from multiple sources and avoid fixating on a single data point.
- Recency Bias: Giving too much weight to recent events can lead to inaccurate predictions.
- Solution: Consider long-term historical data and avoid being swayed by short-term market noise.
- Get Advice: Discuss and review your decision making process.
How Behavioral Finance is Reshaping Modern Investing
The investment world is increasingly recognising the impact of behavioral finance and the role of behavioral biases in investment decision making. Key trends include:
- Integrated Behavioral Coaching: Financial advisors are blending behavioral finance principles into their practice, helping clients make sounder investment decisions. This, combined with enhanced financial literacy, is empowering investors.
- The Rise of Robo-Advisors: These automated platforms minimise emotional biases by executing trades based on algorithms, promoting disciplined investing.
- Behavioral Nudges: These subtle interventions, like auto-enrollment in retirement plans, are designed to encourage better financial decision-making.
- Better Data Analytics: Using your behaviours and trading patterns to identify potential biases.
Capitalizing on Change:
Stay informed about developments in behavioral biases in investment decision making. Embrace technology like AI and robo-advisors to reduce bias. Seek guidance from advisors who understand these principles, and continuously expand your financial knowledge to make smarter investment choices.
Smart Liquidity Strategies to Avoid Behavioral Mistakes
At Forbes Le Brock, we understand that behavioral biases in investment decision making can lead to concentrated investment positions, increasing portfolio risk. While we are not financial advisors, we provide a crucial tool for investors who have already decided to rebalance: strategic liquidity through asset based lending. We empower you to diversify without selling your valuable assets.
Liquidity Solutions Designed to Help You Rebalance Without Selling:
- You Decide, We Provide Liquidity: You’ve analysed your portfolio, identified areas of over-concentration (perhaps due to behavioral biases like overconfidence or herding), and made the strategic decision to diversify. We step in to make that decision a reality.
- Unlock Value Without Selling: Our securities-based lending services for example allow you to access immediate liquidity by using your existing assets as collateral. This means you can rebalance your portfolio without being forced to sell holdings you believe still have long-term potential.
- Flexible and Tailored Solutions: We understand that every investor’s situation is unique. Our lending solutions are tailored to your specific needs and assets, providing flexible terms and repayment options.
- Empowering Your Investment Strategy: We don’t dictate your investment choices. We provide the financial tools that allows you to execute your chosen rebalancing strategy efficiently and effectively.
- Maintain Upside Potential: Keep the asset, and benefit from any future growth.
Example: Diversifying from a Concentrated Tech Position
Imagine an investor, after careful consideration and perhaps consultation with their financial advisor, decides they need to reduce their heavy exposure to tech stocks. They’ve recognised the potential risks (maybe influenced by an understanding of and investment decision bias like herding) and want to diversify into other asset classes.
Here’s how Forbes Le Brock can help:
- Investor’s Decision: The investor independently decides to rebalance their portfolio.
- Liquidity Need: They need capital to invest in other assets but don’t want to sell their tech stocks.
- Forbes Le Brock’s Solution: We provide an asset backed loan, using their tech stocks as collateral. This provides the necessary liquidity without triggering a sale.
- Rebalancing Action: The investor uses the loan proceeds to purchase assets in other sectors, achieving their desired diversification.
- Control and Flexibility: The investor retains ownership of their tech stocks and benefits from any future appreciation. They also have flexible repayment options for the loan.
This approach allows investors to:
- Address Loss Aversion: They avoid the pain of selling assets they believe in.
- Act on Strategic Decisions: They can implement their diversification plan quickly and efficiently.
- Maintain Control: They retain ownership of their original assets.
Forbes Le Brock is your partner in executing your rebalancing strategy, providing the liquidity you need to achieve your desired portfolio allocation, after you’ve made the informed decision to diversify. We empower you to take control of your financial future, free from the constraints of forced asset sales.
Key Takeaways
- Behavioral biases are inherent in human decision-making and can lead to concentrated investment positions, increasing portfolio risk.
- Recognising these biases is crucial for making informed decisions about portfolio diversification and rebalancing.
- A disciplined approach and data is essential to avoid emotional reactions.
- Common pitfalls include overconfidence bias, confirmation bias, loss aversion, herding, and anchoring – all of which can lead to suboptimal portfolio allocation.
- The field of finance is evolving, with a greater understanding of how psychology impacts investment decisions.
- Once you have made the choice, then access to Liquidity is crucial.
- Regular portfolio rebalancing is essential for managing risk and achieving long-term financial goals.
- Asset based lending provides a powerful tool for rebalancing without being forced to sell assets. This allows you to diversify while retaining potential upside.
Conclusion
Don’t let a concentrated portfolio, potentially influenced by hidden biases, limit your financial options.
Once you’ve decided to rebalance and diversify, Forbes Le Brock can help provide the liquidity you need to execute your strategy effectively, without selling your valuable assets. We empower you to take control of your portfolio allocation and achieve your desired investment mix.
Ready to rebalance your portfolio on your terms? Unlock liquidity without selling your assets. Contact Forbes Le Brock today to discuss your options. Serving clients across UK, Europe & Asia-Pacific
🎙️ Prefer an audio summary? Check out a Deep Dive into Behavioral Biases in Investment Decision Making. 🎧 Listen now!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are behavioral biases in investment decision making?
Behavioral biases are systematic patterns of deviation from rational judgment that influence investment decisions. These biases often lead to suboptimal portfolio allocations by causing investors to make emotionally-driven or irrational choices. - What are cognitive biases, and how do they differ from behavioral biases in investing?
Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts or systematic errors in thinking that deviate from rationality. While cognitive biases relate to how we process information, behavioral biases focus on the decisions and actions that result from those thought patterns. Many behavioral biases in investing stem from underlying cognitive biases. For example, confirmation bias (a cognitive bias) may cause an investor to hold onto losing investments longer than advisable, a behavioral bias known as the disposition effect. Understanding cognitive biases is key to recognising when rebalancing may be necessary. - How does overconfidence bias affect investment decisions?
Overconfidence bias leads investors to overestimate their knowledge and abilities. This often results in taking excessive risks or maintaining overly concentrated positions, which can increase portfolio vulnerability. - What is confirmation bias in finance?
Confirmation bias is the tendency to favour information that confirms existing beliefs while disregarding contradictory data. In investing, this can cause a portfolio to become overly concentrated in certain assets or sectors, reducing diversification. - How can I overcome loss aversion when considering portfolio rebalancing?
Loss aversion describes the tendency to feel losses more intensely than gains. This can make selling assets difficult, even when rebalancing is strategically advantageous. Asset-based lending offers a solution by providing liquidity without the need to sell, enabling portfolio diversification while holding onto your investments. - What is the role of behavioral finance in investment?
Behavioral finance examines how psychological factors influence financial decisions. By understanding these influences, investors can make more informed and disciplined choices, improving long-term investment outcomes.
