
Fundamentals of Real Estate Finance: A Guide for Investors and Property Developers
Real estate finance is a critical component of the property market, enabling investors and developers to acquire, develop, and manage properties effectively. Whether you’re a first-time investor or an experienced developer, understanding the different financing options, structures, and risk factors is essential for making informed decisions.
Types of Real Estate Financing
1. Traditional Bank Loans
Banks provide real estate financing through term loans or mortgages. These loans usually require a strong credit history, collateral, and a well-defined repayment structure. Interest rates vary based on market conditions and borrower risk profiles.
2. Private Lending
Private lenders offer more flexible financing solutions compared to traditional banks. These loans typically have higher interest rates but are faster to secure, making them ideal for investors needing quick capital.
3. Hard Money Loans
Hard money loans are short-term, asset-based loans primarily used for real estate investments like fix-and-flip projects. These loans are secured by the property itself rather than the borrower’s creditworthiness.
4. Bridge Loans
Bridge loans help investors cover financial gaps between purchasing a new property and selling an existing one. They are short-term and come with higher interest rates but provide liquidity when needed.
5. Mezzanine Financing
Mezzanine financing combines debt and equity, often used in large-scale developments. Investors receive subordinated debt with an option to convert it into equity if repayment obligations are not met.
6. Real Estate Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding platforms allow multiple investors to pool funds for property investments. This option democratizes real estate investing, enabling individuals to invest in high-value properties with smaller amounts.
Key Factors in Real Estate Financing
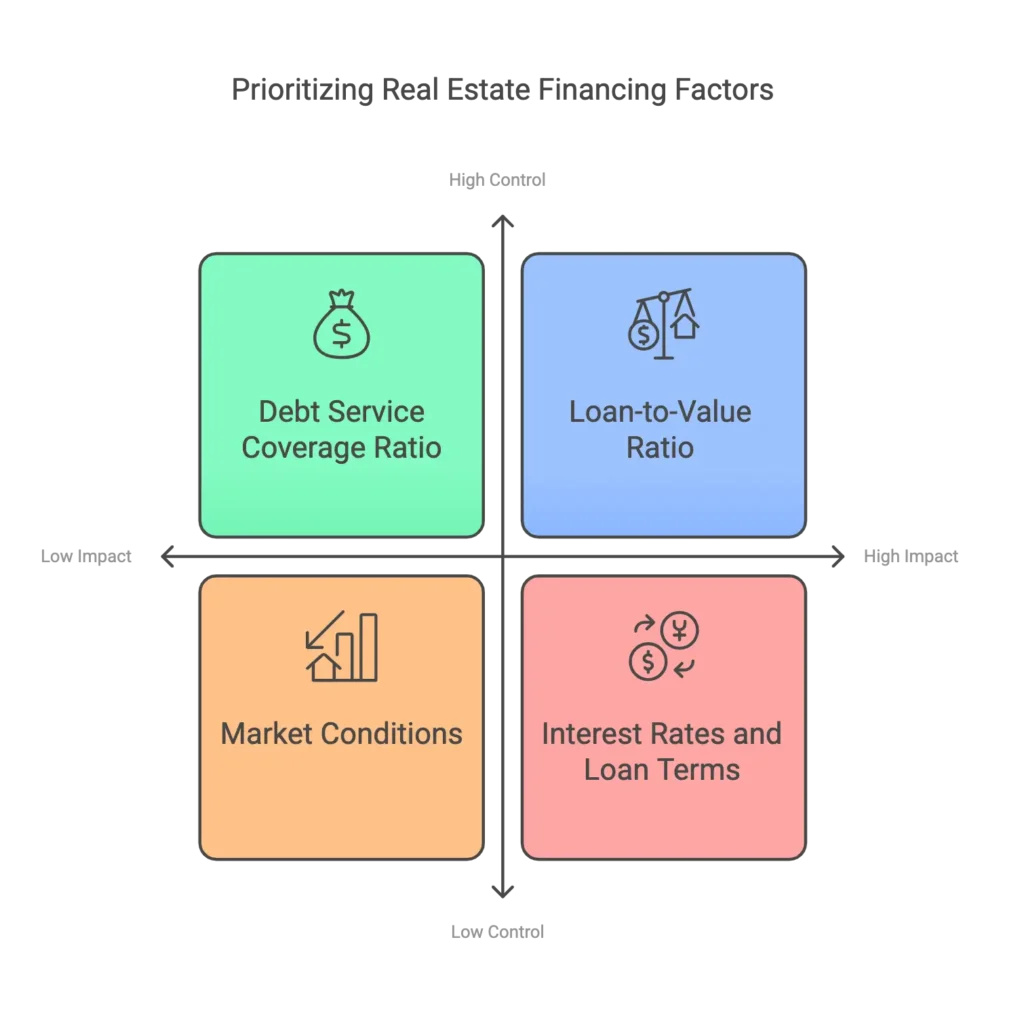
1. Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV)
LTV measures the risk level of a loan by comparing the loan amount to the property’s value. A lower LTV ratio indicates less risk for lenders and often results in better loan terms.
2. Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR)
DSCR is used to assess a property’s ability to generate enough income to cover debt payments. Lenders prefer a DSCR above 1.25 for safe lending.
3. Interest Rates and Loan Terms
Fixed vs. variable interest rates impact loan affordability. Longer loan terms reduce monthly payments but may increase overall interest costs.
4. Market Conditions
Economic factors, such as inflation, interest rate hikes, and property demand, affect financing costs and availability.
Risks and Challenges in Real Estate Finance
- Market Volatility: Property values fluctuate based on economic conditions, impacting financing and investment returns.
- Regulatory Changes: New laws and lending restrictions can alter financing structures.
- Credit Risk: Borrowers with weak credit profiles may struggle to secure favorable loan terms.
- Liquidity Issues: Illiquid assets make quick exits difficult, especially in downturns.
Conclusion
Understanding real estate finance is crucial for investors and developers looking to navigate the complexities of the property market. By evaluating financing options, key metrics, and risks, you can make informed investment decisions and optimize returns. Whether leveraging traditional bank loans, private lending, or alternative financing solutions, a strategic approach will ensure financial success in real estate ventures.
If you’re exploring financing options for your next project, contact us today to discuss tailored solutions that fit your investment goals.
Q&A: Real Estate Financing
What are the main types of real estate financing?
✔ Traditional Bank Loans – Require strong credit, collateral, and structured repayment terms.
✔ Private Lending – More flexible but higher interest rates, ideal for quick funding.
✔ Hard Money Loans – Short-term, asset-based financing for fix-and-flip projects.
✔ Bridge Loans – Covers gaps between buying and selling properties, with higher interest rates.
✔ Mezzanine Financing – A mix of debt and equity, often used for large developments.
✔ Real Estate Crowdfunding – Pools investments from multiple investors to finance projects.
How do lenders assess real estate loans?
🔹 Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV): Compares loan amount to property value; lower LTV means lower risk.
🔹 Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR): Measures a property’s income against debt payments; lenders prefer DSCR above 1.25.
🔹 Interest Rates & Loan Terms: Fixed vs. variable rates impact affordability and total cost.
🔹 Market Conditions: Economic trends affect interest rates and financing availability.
What are the key risks in real estate finance?
⚠ Market Volatility: Property values fluctuate, affecting returns.
⚠ Regulatory Changes: Lending laws can shift financing requirements.
⚠ Credit Risk: Poor borrower credit history leads to unfavourable terms.
⚠ Liquidity Issues: Selling real estate quickly can be difficult, especially in downturns.
How can investors optimize their financing strategy?
✅ Compare financing options based on cost, speed, and flexibility.
✅ Maintain strong credit and financial records for better loan terms.
✅ Diversify funding sources to mitigate risk.
✅ Stay informed about market conditions and regulations.
How can we help with real estate financing?
💬 If you’re exploring real estate finance options for your next project, contact us today for tailored solutions that fit your investment goals.
